

The purpose of the Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA) is to identify and address movement dysfunctions in individuals. It is a comprehensive assessment tool that helps healthcare professionals, such as physical therapists and chiropractors, to evaluate and understand how a person moves and identify any limitations or dysfunctions that may be contributing to pain or decreased performance.
The SFMA differs from other movement assessments in its systematic approach and focus on identifying the root cause of movement dysfunctions. Unlike other assessments that may only look at specific joints or movements, the SFMA evaluates the entire body as a whole, recognizing that movement dysfunctions in one area can affect other areas. It also incorporates both active and passive movements to assess mobility and stability, providing a more comprehensive understanding of an individual's movement patterns.
By Professional Physical Therapy Professional Physical Therapy is proud to announce the celebration of its 25th anniversary, January 2024, marking a quarter-century of providing exceptional care and rehabilitation services to their communities throughout New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire. Since the opening of their first clinic in 1999, Professional has been dedicated … Continued The post Professional Physical Therapy Celebrates 25 Years of Excellence in Patient Care appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-26
By Professional Physical Therapy In today’s fast-paced world, finding a balance between staying active and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be challenging. Yet, within these challenges lie numerous opportunities to transform our routines and bolster our well-being. We unveil 25 essential tips that serve as steppingstones toward a more active and healthier lifestyle. Each tip … Continued The post 25 Essential Tips to Live a More Active & Healthy Life appeared first on Professional Physical Therapy.
Posted by on 2023-12-26
The key components of the SFMA include a series of movement tests and assessments that evaluate different movement patterns and positions. These include tests for mobility, stability, and motor control. The SFMA uses a top-down approach, starting with global movements and then breaking them down into more specific tests to identify any dysfunctions or limitations.
SF Bay-Area Rehabilitative Healthcare Clinics Lead The Industry In Research and Patient Care
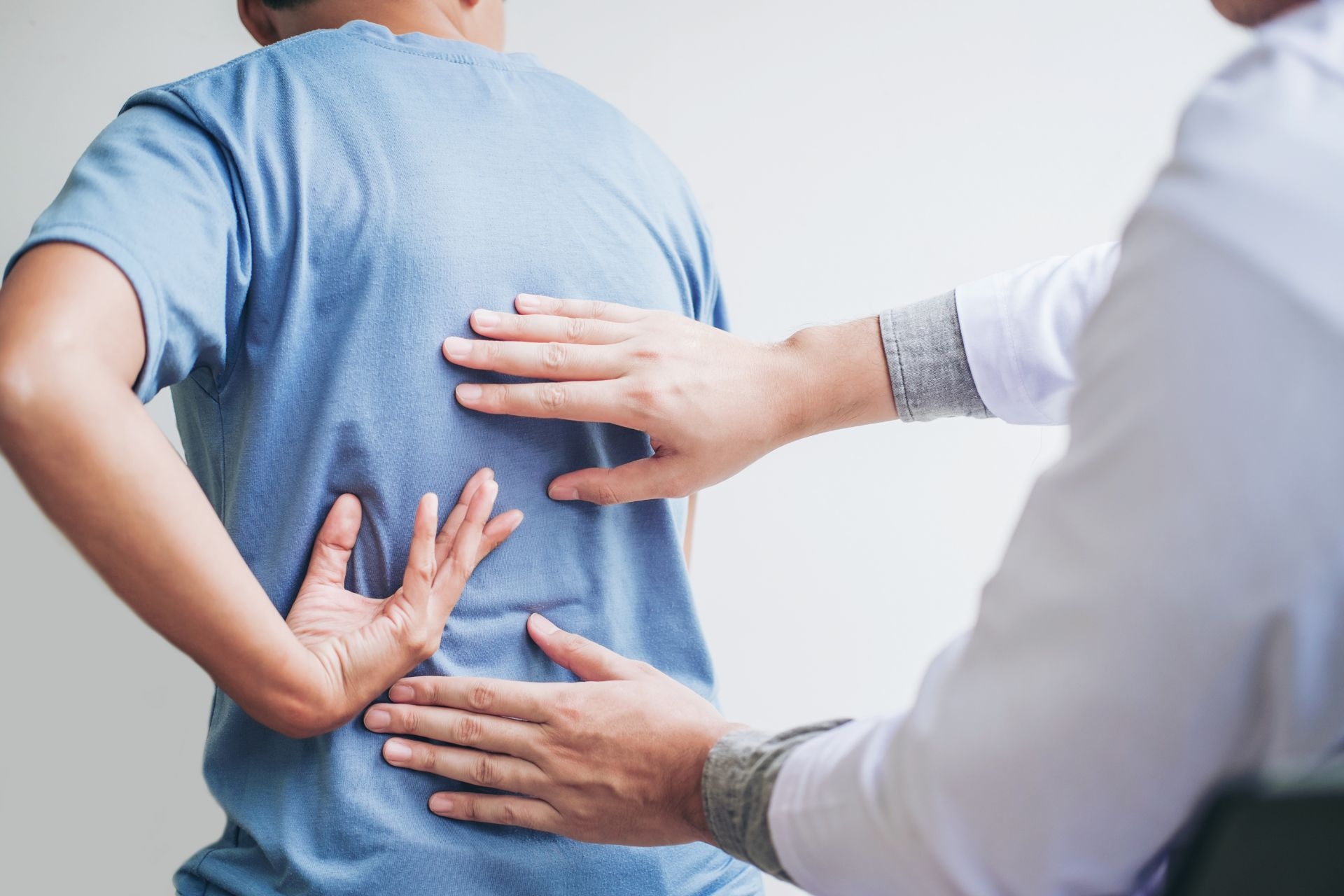
The SFMA is used to identify movement dysfunctions by assessing how an individual moves and identifying any limitations or asymmetries in their movement patterns. It looks for patterns of movement dysfunction rather than focusing on specific diagnoses or injuries. By identifying these dysfunctions, healthcare professionals can develop targeted treatment plans to address the underlying causes of pain or decreased performance.
Yes, the SFMA can be used for individuals of all ages and fitness levels. It is a versatile assessment tool that can be adapted to meet the needs of different populations. Whether someone is a professional athlete or a sedentary individual, the SFMA can help identify movement dysfunctions and guide the development of an appropriate treatment plan.

While the SFMA is a valuable assessment tool, there are some limitations and contraindications to consider. It may not be suitable for individuals with acute injuries or severe pain, as it involves active movements that could exacerbate their condition. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions or limitations may not be able to perform all the tests in the SFMA. It is important for healthcare professionals to consider these factors and adapt the assessment as needed.
The results of the SFMA can be used to develop a treatment plan by providing valuable information about an individual's movement dysfunctions. By understanding the specific limitations and dysfunctions identified through the assessment, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to address these issues. This may include a combination of manual therapy, corrective exercises, and movement re-education to improve mobility, stability, and motor control. The treatment plan can be tailored to the individual's specific needs and goals, helping them to improve their movement patterns and overall function.

Yes, there are specific exercises that can be used in physical therapy to help prevent falls in elderly patients. These exercises focus on improving balance, strength, and flexibility, which are all important factors in maintaining stability and reducing the risk of falls. Some examples of exercises that may be included in a fall prevention program for elderly patients include standing on one leg to improve balance, heel-to-toe walking to enhance coordination, and leg lifts to strengthen the lower body muscles. Additionally, exercises that target core stability, such as abdominal and back exercises, can also be beneficial in improving overall balance and stability. Physical therapists may also incorporate functional exercises that simulate real-life movements, such as stepping over obstacles or navigating uneven surfaces, to help patients develop the necessary skills to prevent falls in their daily activities.
In physical therapy, various stretches are recommended for individuals experiencing lower back pain. These stretches aim to alleviate discomfort, improve flexibility, and strengthen the muscles in the lower back region. Some commonly recommended stretches include the knee-to-chest stretch, where the individual lies on their back and brings one knee towards their chest, holding the position for a few seconds before switching to the other leg. Another effective stretch is the cat-camel stretch, where the individual gets on all fours and alternates between arching their back upwards like a cat and then dropping it downwards like a camel. Additionally, the child's pose stretch, where the individual kneels on the floor and sits back on their heels while reaching their arms forward, can also help relieve lower back pain. These stretches, along with others recommended by a physical therapist, can provide relief and aid in the recovery process.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in addressing balance deficits in individuals with peripheral neuropathy. The therapy focuses on improving proprioception, which is the body's ability to sense its position in space. This is achieved through a variety of exercises that target the sensory receptors in the muscles, joints, and tendons. These exercises may include balance training, such as standing on one leg or using unstable surfaces, to challenge and improve the individual's balance. Additionally, physical therapists may incorporate gait training to enhance the individual's ability to walk safely and efficiently. Strengthening exercises for the lower extremities are also commonly prescribed to improve muscle control and stability. Furthermore, therapists may utilize manual techniques, such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations, to address any restrictions or imbalances that may be contributing to the balance deficits. Overall, physical therapy aims to optimize the individual's functional abilities and reduce the risk of falls by addressing the underlying balance deficits associated with peripheral neuropathy.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) arthritis by employing various techniques to alleviate pain, improve joint mobility, and enhance overall function. Through a combination of manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities, physical therapists aim to reduce inflammation, restore normal joint mechanics, and strengthen the surrounding muscles. Manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilizations and soft tissue mobilizations help to improve joint range of motion and reduce pain. Therapeutic exercises, including jaw stretching and strengthening exercises, promote muscle relaxation and enhance joint stability. Additionally, modalities such as heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation may be utilized to further reduce pain and inflammation. By addressing the underlying causes and symptoms of TMJ arthritis, physical therapy provides individuals with effective management strategies to improve their quality of life.
Physical therapy takes a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation after a shoulder dislocation. The therapist will first assess the extent of the injury and develop a personalized treatment plan that may include exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder joint. The therapist may also use modalities such as ice, heat, and electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation. Additionally, the therapist may incorporate manual therapy techniques such as massage and joint mobilization to improve tissue healing and restore normal joint mechanics. As the patient progresses, the therapist may also incorporate functional exercises to simulate real-life activities and help the patient regain full function of the shoulder. Overall, physical therapy aims to restore the patient's shoulder function and prevent future dislocations through a combination of targeted exercises, modalities, and manual therapy techniques.
Integrating virtual reality technology into physical therapy sessions requires adherence to several best practices to ensure optimal outcomes. Firstly, therapists should carefully select virtual reality programs that are specifically designed for rehabilitation purposes, incorporating exercises and activities that target the patient's specific needs and goals. It is crucial to consider the patient's condition, such as musculoskeletal injuries or neurological impairments, when choosing the appropriate virtual reality applications. Additionally, therapists should provide proper instruction and guidance to patients on how to use the virtual reality equipment effectively and safely. This includes educating patients on correct body mechanics and posture during virtual reality exercises to prevent any potential injuries. Regular monitoring and assessment of the patient's progress and adjusting the virtual reality program accordingly is also essential for maximizing therapeutic benefits. By following these best practices, physical therapists can effectively integrate virtual reality technology into their sessions, enhancing patient engagement, motivation, and overall rehabilitation outcomes.